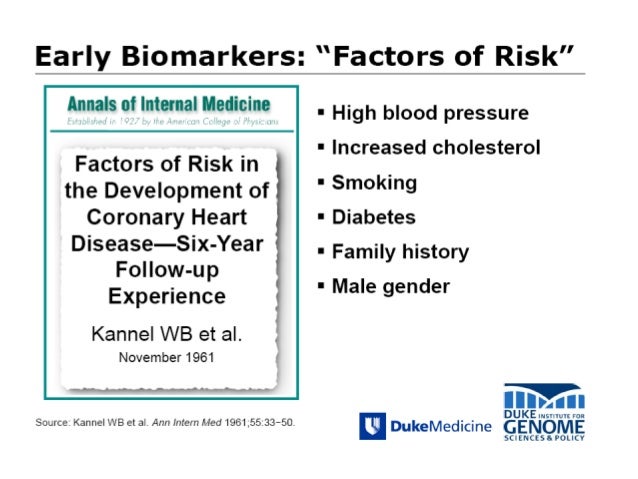
Lifetime Risk Of Developing Coronary Heart Disease
Lifetime risk of developing coronary heart disease. Preeclampsia a condition that can happen during pregnancy and is linked to an increased lifetime risk for coronary heart disease. The Framingham risk score stratified lifetime risk well for women at all ages. Sanchez-Delgado E Liechti H.
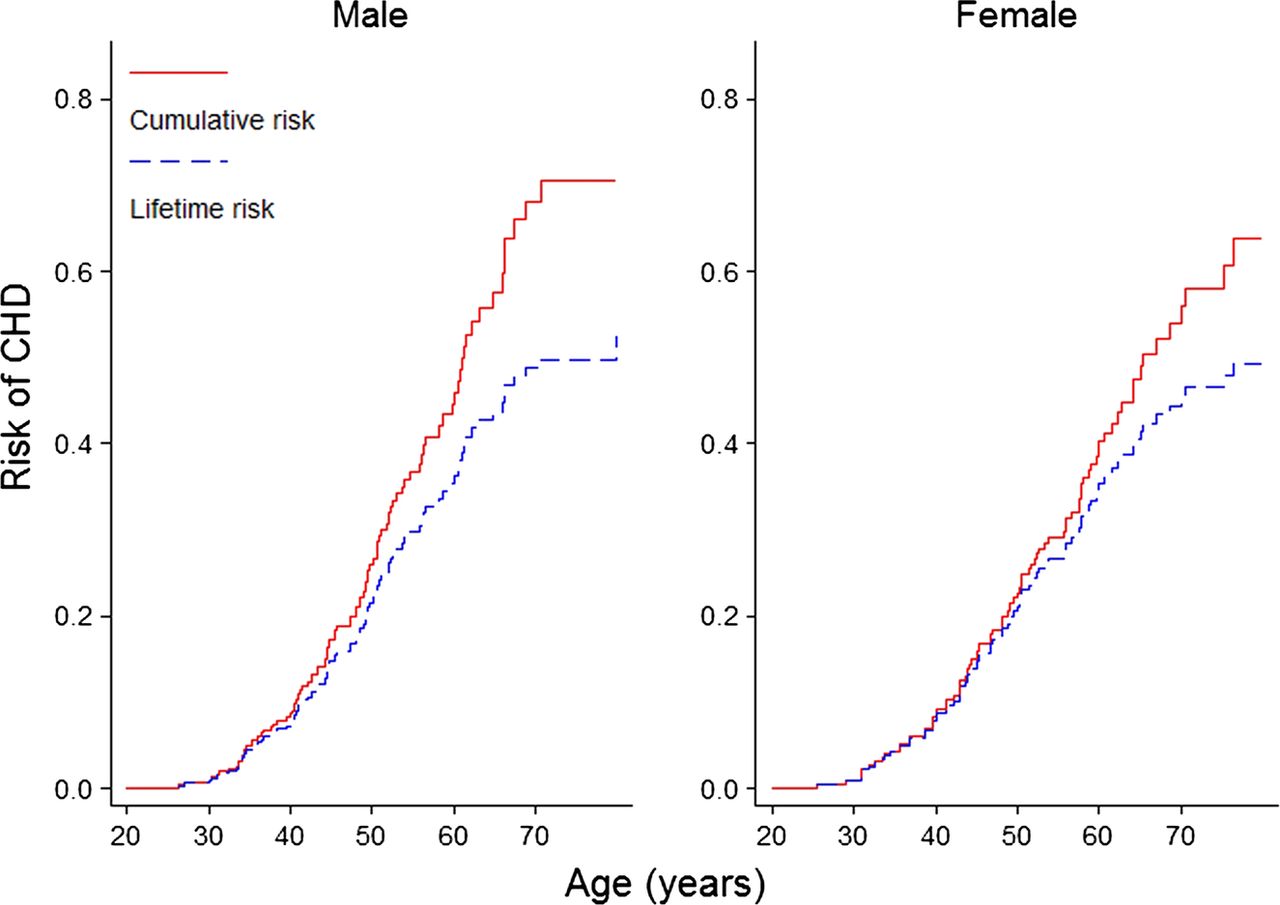
5 linhas The risk of developing coronary heart disease before age 40 years was low 12 in men 02 in. Curves for smokers and non-smokers with UK population mean values for total and HDL-cholesterol and blood pressure BP. Lifetime cumulative risk without adjusting for competing risk was 707 for men and 638 for women.
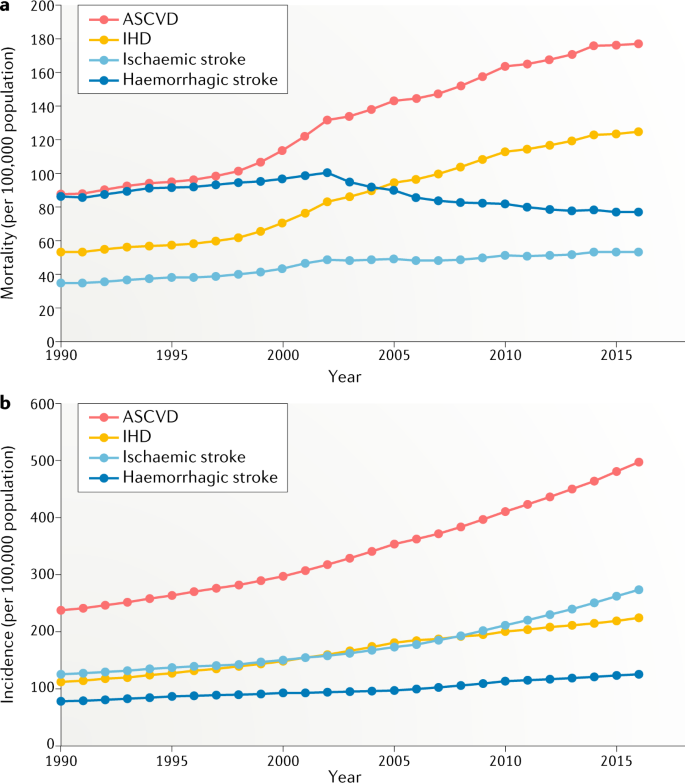
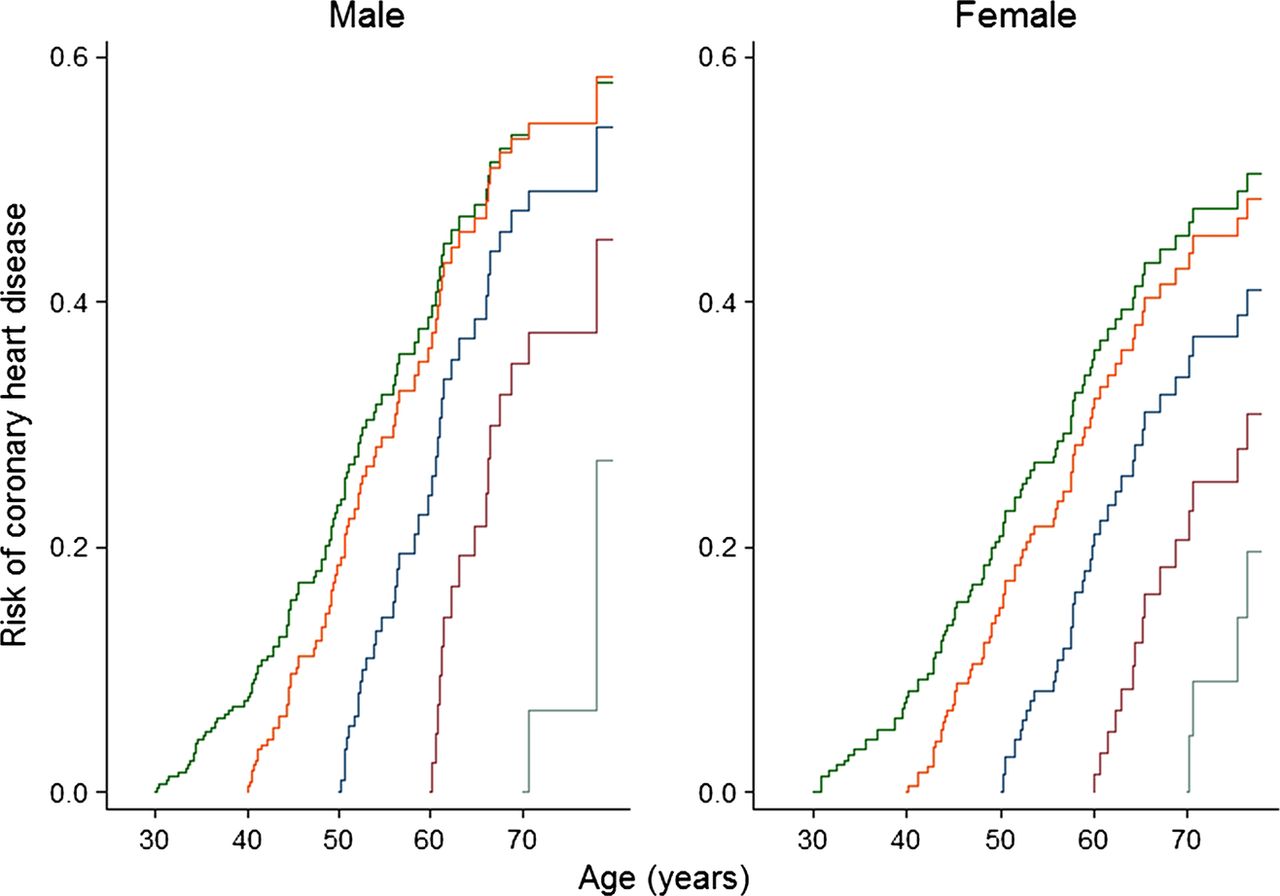
At age 70 years lifetime risk was. 10094005 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types. The risk of developing CHD increased with age until 60 years and then decreased with age.
As we stated in the final paragraph of our article the results of lifetime risk analyses stratified by risk factor status eg for smokers and nonsmokers are not predictable since characteristics such as smoking that modify the risk of coronary heart disease also modify the risk of death from. Figure Cumulative risk of coronary heart disease baseline age 40 years Show full caption. After we excluded isolated angina pectoris as an initial event the lifetime risk of coronary artery disease events at age 40 years was.
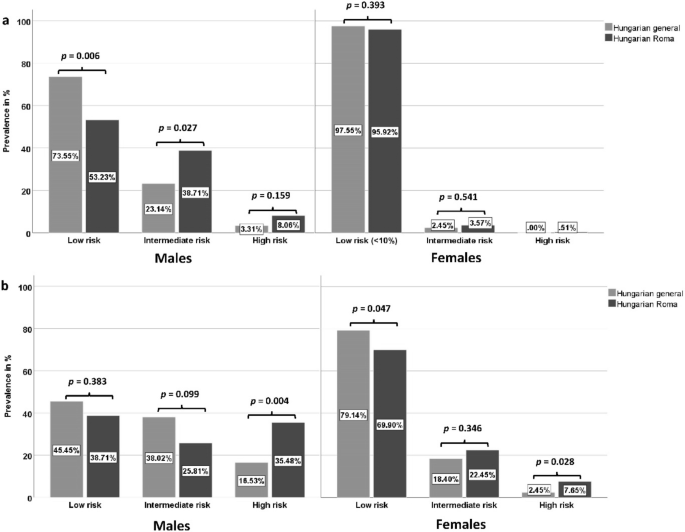
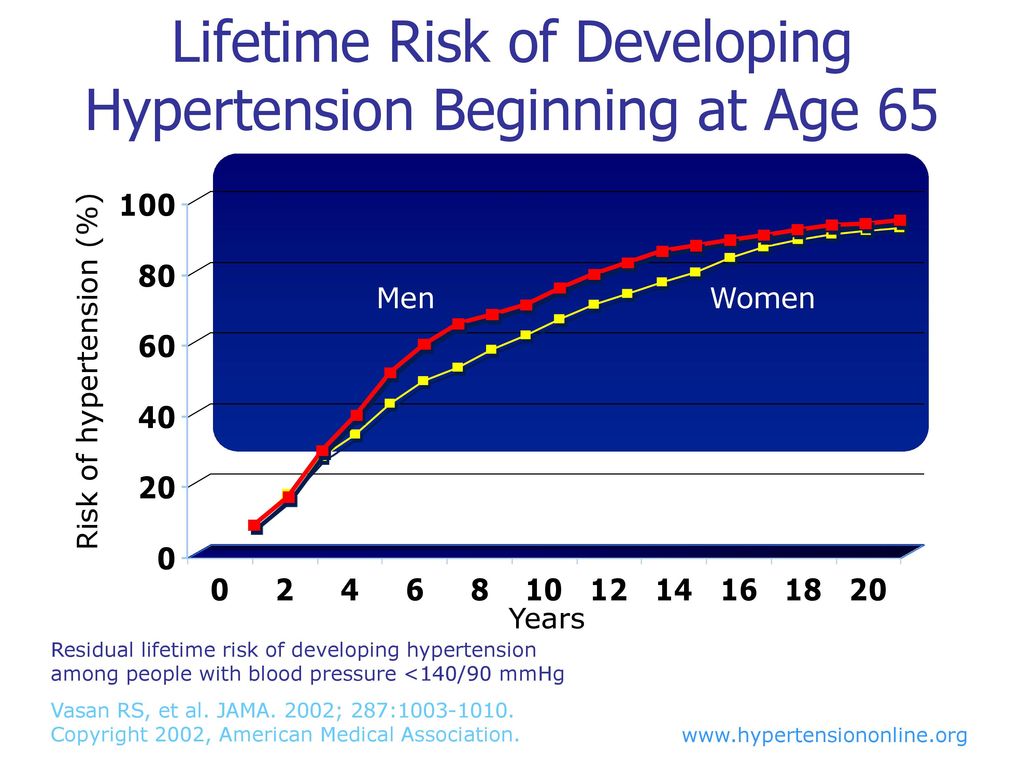
We assessed cumulative and total lifetime risk and the age at which cumulative risk reached 25 R 25. At age 70 years lifetime risk was 349 312387 for men and 242 214270 for women. Lifetime risk is high in Aboriginal men and women with one in two developing coronary heart disease CHD during their lifetime.
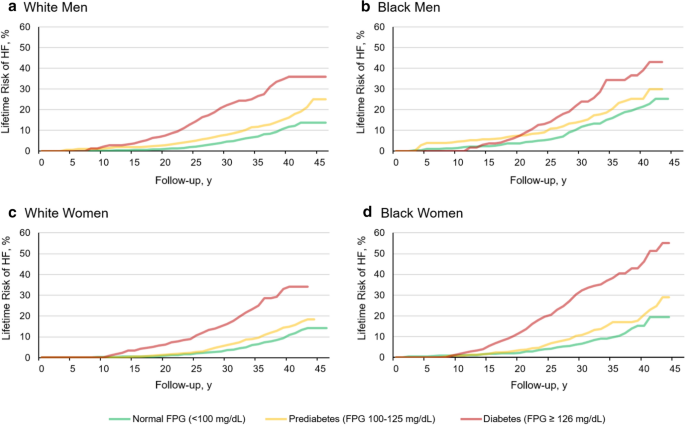
Lifetime risk of developing coronary heart disease. Early menopause before age 40. In this study obesity was associated with shorter longevity and significantly increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality compared with normal BMI.
At age 40 years in risk score tertiles 1 2 and 3 respectively the lifetime risks for CHD were 384 417 and 507 for men and 122 254 and 332 for women. Those with an optimal risk-factor profile also had lower lifetime risks of fatal coronary heart disease or nonfatal myocardial infarction 36.
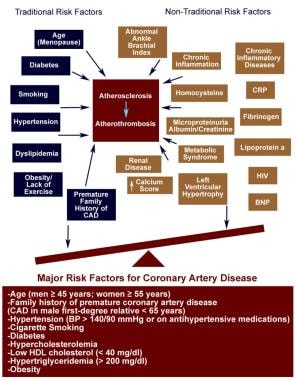
Calcium scoring is perhaps one of the best prognosticating indicators for heart disease in patients who are young with a family history as well as in people with diabetes over the age of 40.
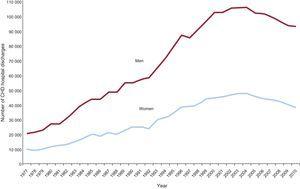
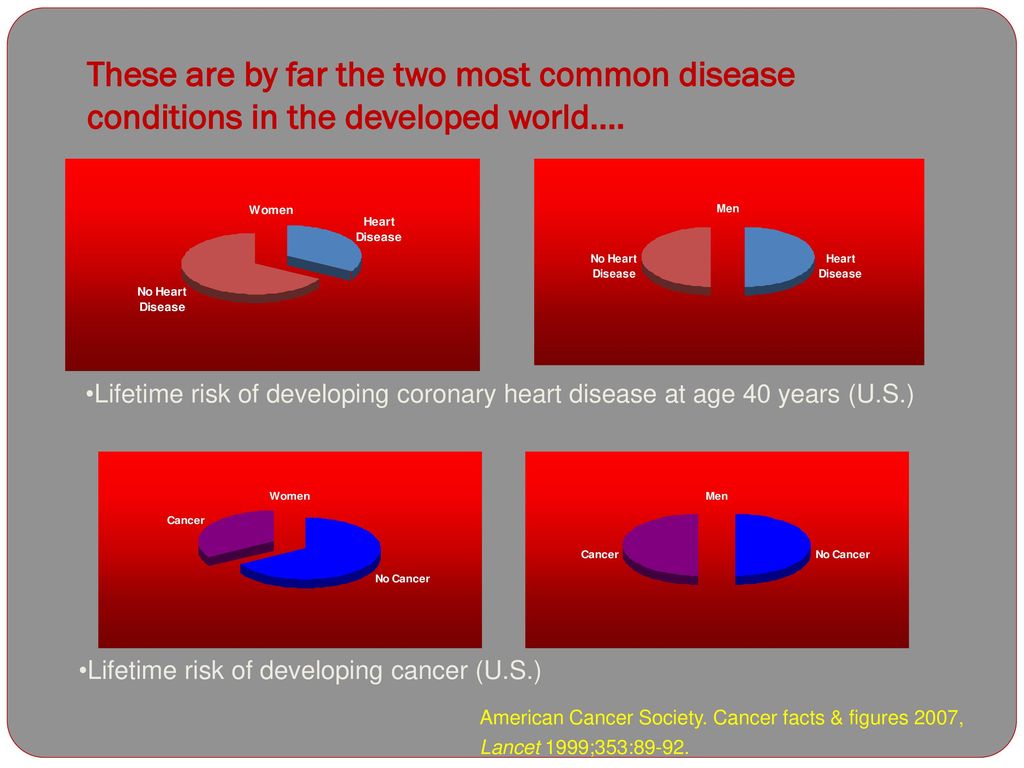
Lifetime risk of coronary heart disease at age 40 years was 486 95 CI 458-513 for men and 317 292-342 for women. Sanchez-Delgado E Liechti H. Figure Cumulative risk of coronary heart disease baseline age 40 years Show full caption. Calcium scoring is perhaps one of the best prognosticating indicators for heart disease in patients who are young with a family history as well as in people with diabetes over the age of 40. In this study obesity was associated with shorter longevity and significantly increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality compared with normal BMI. Lifetime risk of coronary heart disease at age 40 years was 486 95 CI 458513 for men and 317 292342 for women. Lifetime risk of coronary heart disease at age 40 years was 486 95 CI 458-513 for men and 317 292-342 for women. Lifetime cumulative risk without adjusting for competing risk was 707 for men and 638 for women. The average age at which the first CHD event occurs is under 50 years 48 years for men and 49 for women which is much younger than those reported in other populations 65 years in men and 70 years in women in the Framingham Study.
Lifetime risk of coronary heart disease at age 40 years was 486 95 CI 458513 for men and 317 292342 for women. Lifetime risk of coronary heart disease at age 40 years was 486 95 CI 458-513 for men and 317 292-342 for women. Association of Body Mass Index With Lifetime Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Compression of Morbidity. Oxygen and blood nutrients are supplied to the heart muscle through the coronary arteries. Sanchez-Delgado E Liechti H. In this study obesity was associated with shorter longevity and significantly increased risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality compared with normal BMI. The Framingham risk score stratified lifetime risk well for women at all ages.





















.svg)








Post a Comment for "Lifetime Risk Of Developing Coronary Heart Disease"