Congestive Heart Failure Liver Disease
Congestive heart failure liver disease. However subclinical asymptomatic decline will have already been in place from years of poor cardiac output. Longstanding heart failure can actually result in a sudden decline in liver function. Haemodynamic disturbances in heart failure and mechanisms resulting in different patterns of elevated liver enzymes.
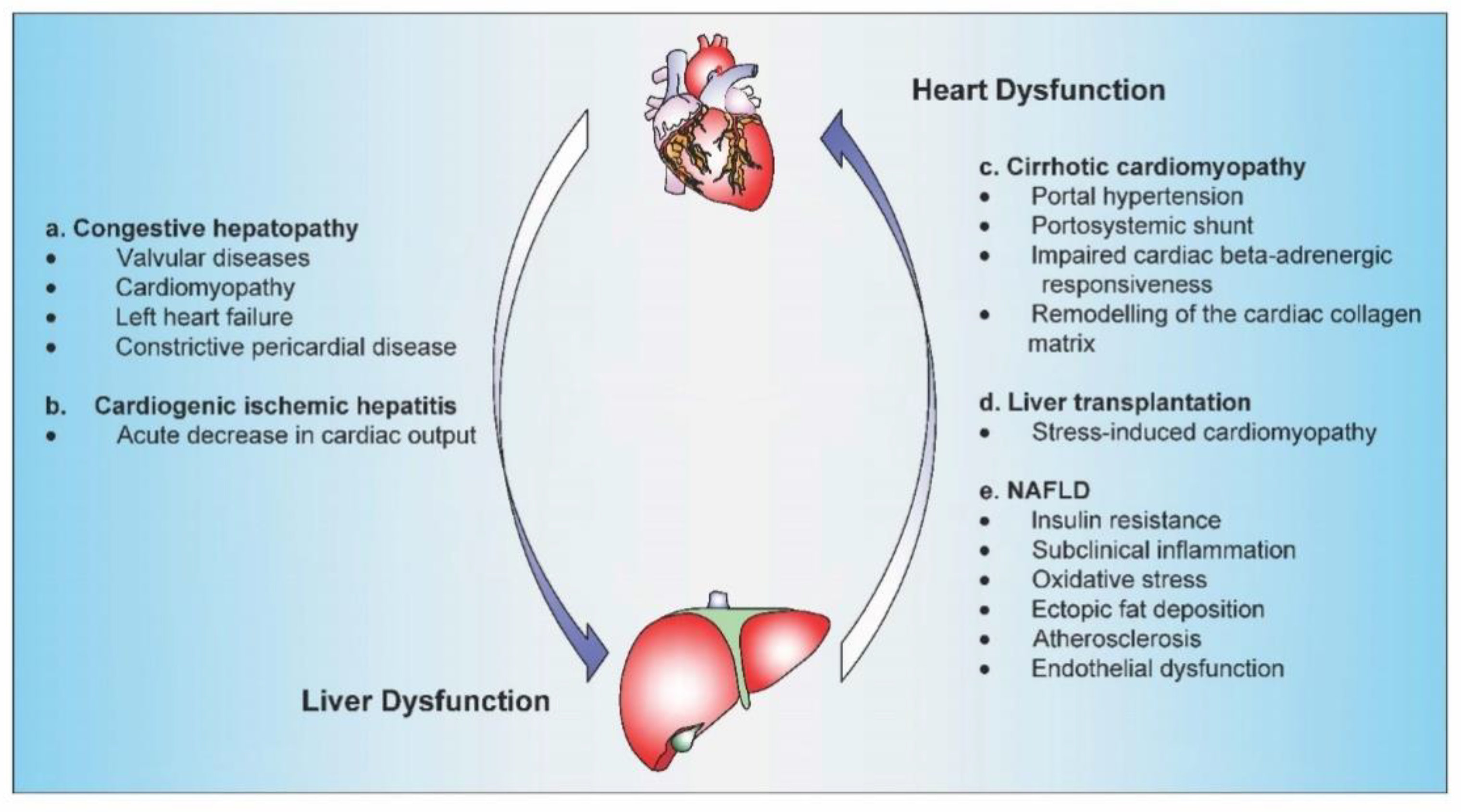
Heart failure is a chronic condition caused by a weakened heart muscle. Jackson L Branch R Levine D Ramsay L. No accepted specific treatment of cirrhotic cardiomyopathy exists.
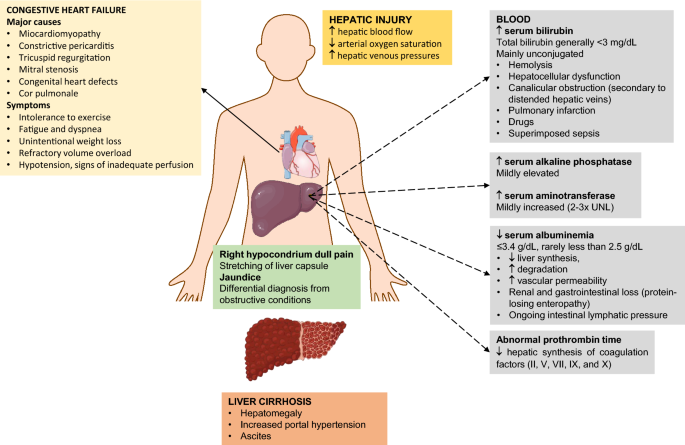
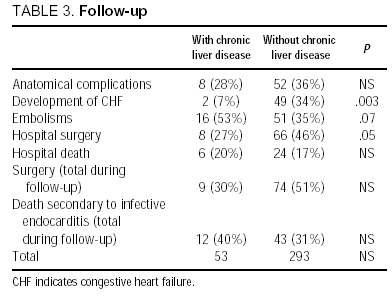
To synthesize data addressing outcomes of metformin use in populations with type 2 diabetes and moderate to severe chronic kidney disease CKD congestive heart failure CHF or chronic liver disease CLD with hepatic impairment. As heart failure progresses the hearts ability to pump blood to the body progressively deteriorates and other organs suffer. Only about 5 of patients with hepatic disease and CHF will have clinically overt jaundice but up to 70 of patients may have a mild increase in unconjugated bilirubinemia.
Elimination of canrenone in congestive heart failure and chronic liver disease. The elimination half-life T12 of canrenone the principal unconjugated metabolite of spironolactone was 59 h range 32-105 h in 5 patients with chronic liver disease and 37 h range 19-48 h in 7 patients withcongestive heart failure. Elevated Liver Enzymes and Congestive Heart Failure Congestive Heart Failure.
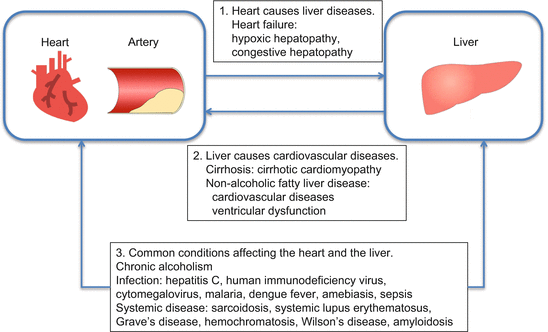
In their clinical practice physicians can face heart diseases chronic or acute heart failure affecting the liver and liver diseases affecting the heart. It can no longer be productive on reduced blood flow. Therefore it is crucial in clinical practice to identify complex interactions between heart and liver in order to provide the best treatment for both.
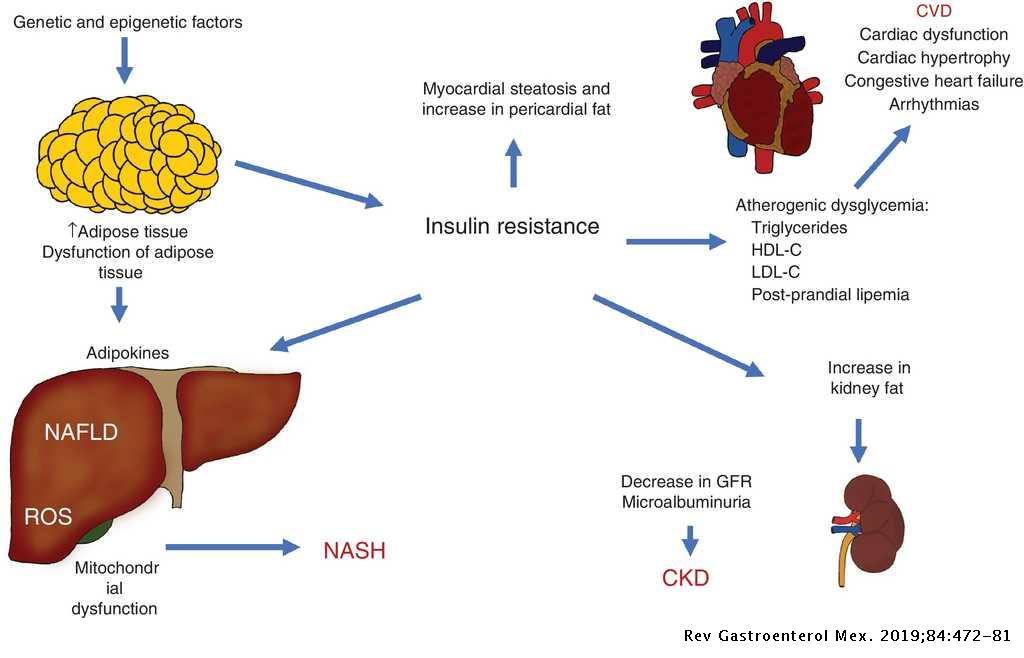
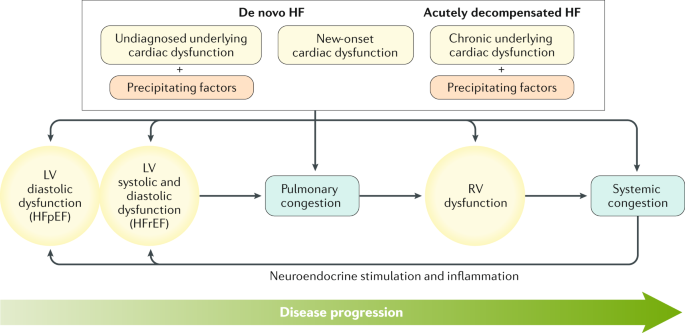
Broadly speaking the term refers to any form of liver damage that occurs in a person with cardiac problems as a result of the cardiac problem. Heart failure HF is a systemic disorder caused by the inability of the heart to accommodate the venous return and to maintain sufficient cardiac output to meet the bodys metabolic needs. Heart failure HF and liver disease often co-exist because of systemic disorders and diseases that affect both organs alcohol abuse drugs inflammation autoimmunity infections as well as because of complex cardiohepatic interactions.
Thus it appears that hepatic congestion secondary to right-sided heart disease may prime the liver for ischemic insults from low cardiac output and reduced hepatic blood flow and oxygenation due to left-sided heart failure. In congestive heart failure the heart has an impaired ability to deliver blood to the body.
General Effects on Organs.
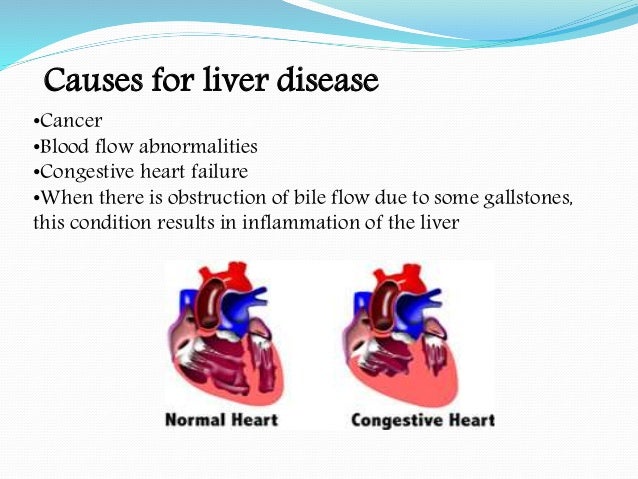
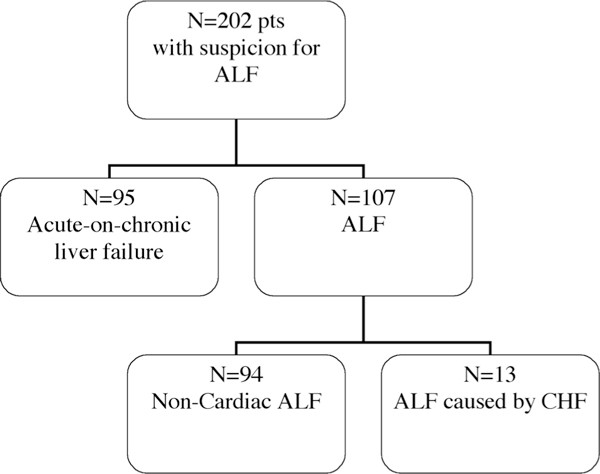
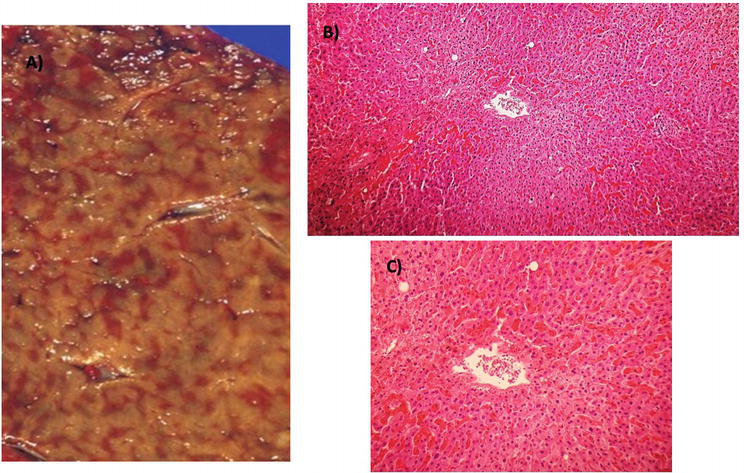
It can no longer be productive on reduced blood flow. There are several well-recognized forms of vascular injury to the liver including Budd-Chiari syndrome hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome passive congestion due to heart failure hepatic infarction and ischemic hepatitis. The prognosis of the patients with cirrhotic cardiomyopathy is affected by heart failure which can develop during invasive procedures surgery insertion of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting and liver transplantation. Elevated Liver Enzymes and Congestive Heart Failure Congestive Heart Failure. They share many of the same risk factors. It can no longer be productive on reduced blood flow. That is a professional way of saying it is a liver disease caused by congestion particularly venous congestion. The elimination half-life T12 of canrenone the principal unconjugated metabolite of spironolactone was 59 h range 32-105 h in 5 patients with chronic liver disease and 37 h range 19-48 h in 7 patients withcongestive heart failure. Only about 5 of patients with hepatic disease and CHF will have clinically overt jaundice but up to 70 of patients may have a mild increase in unconjugated bilirubinemia.
And some treatment approaches are helpful for both. Cardiac cirrhosis is also known as congestive hepatopathy. Coronary artery disease CAD and congestive heart failure are two common heart conditions. The prognosis of the patients with cirrhotic cardiomyopathy is affected by heart failure which can develop during invasive procedures surgery insertion of a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting and liver transplantation. However subclinical asymptomatic decline will have already been in place from years of poor cardiac output. Heart failure HF and liver disease often co-exist because of systemic disorders and diseases that affect both organs alcohol abuse drugs inflammation autoimmunity infections as well as because of complex cardiohepatic interactions. In congestive heart failure the heart has an impaired ability to deliver blood to the body.























/what-is-congestive-heart-failure-1746188_final-f16c287db5014fed8ea46293ce78ebbd.png)





Post a Comment for "Congestive Heart Failure Liver Disease"