Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy Syndrome
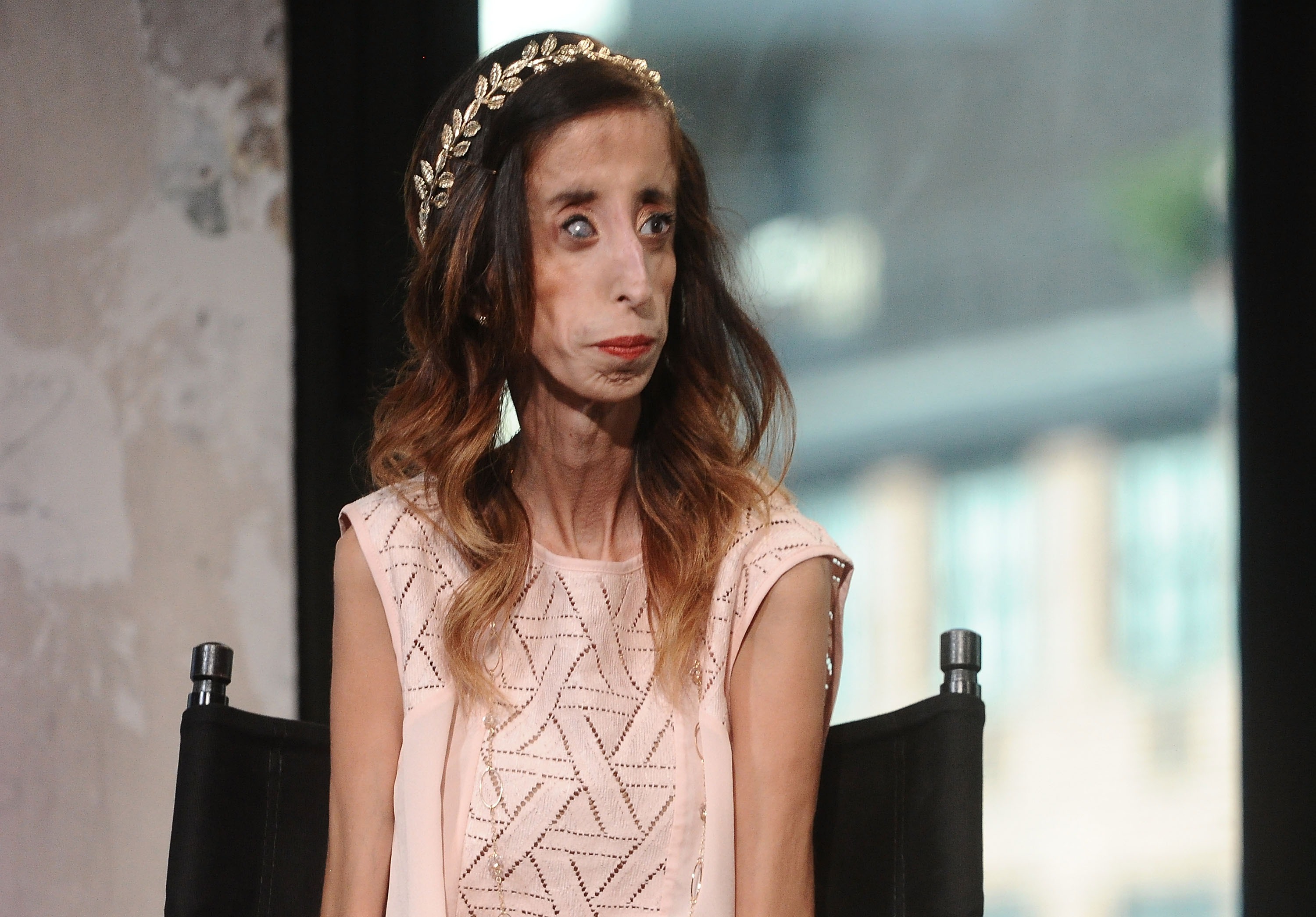
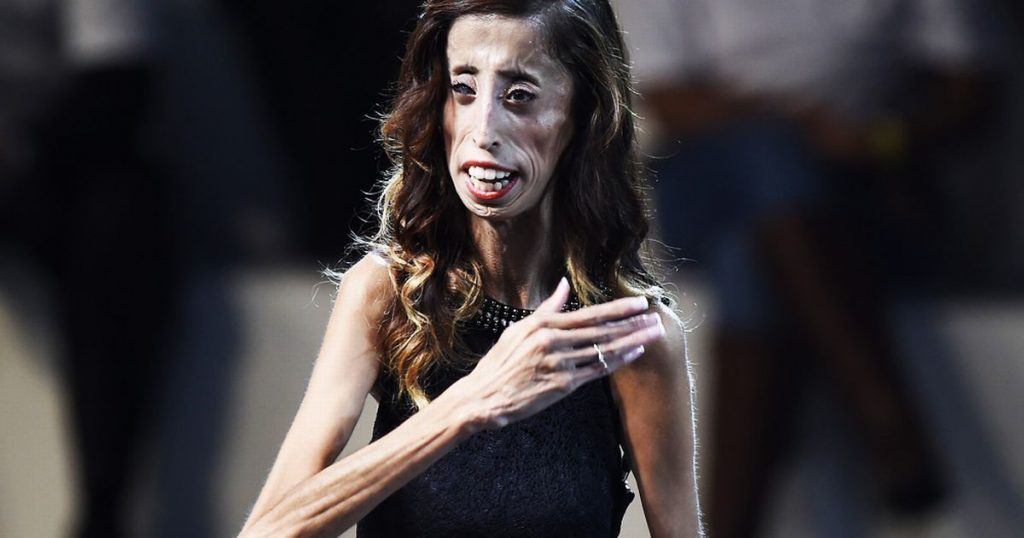
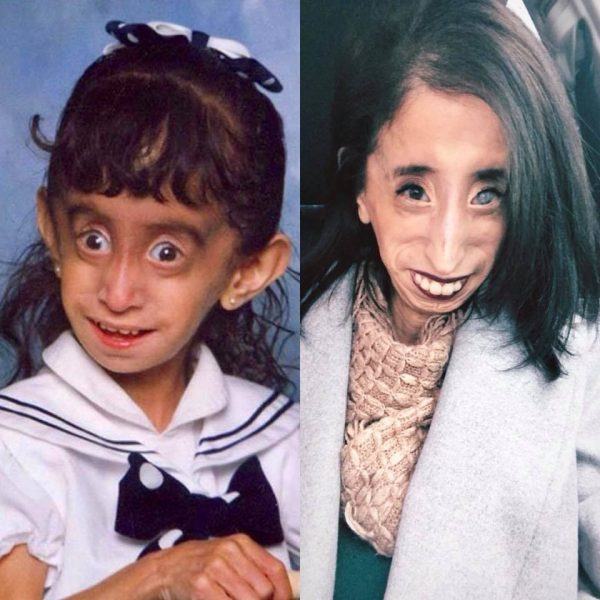
Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy syndrome. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin with long arms legs fingers and toes. Neonatal progeroid variant of Marfan syndrome with congenital lipodystrophy results from mutations at the 3 end of FBN1 gene. An autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by congenital lipodystrophy a progeroid facial appearance due to lack of subcutaneous fat and variable signs of Marfan syndrome.
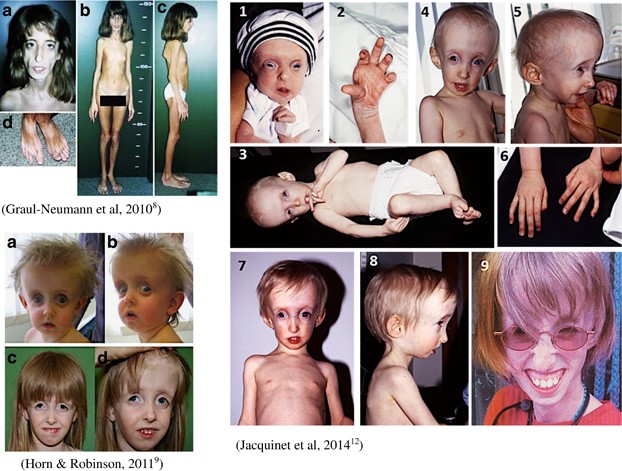
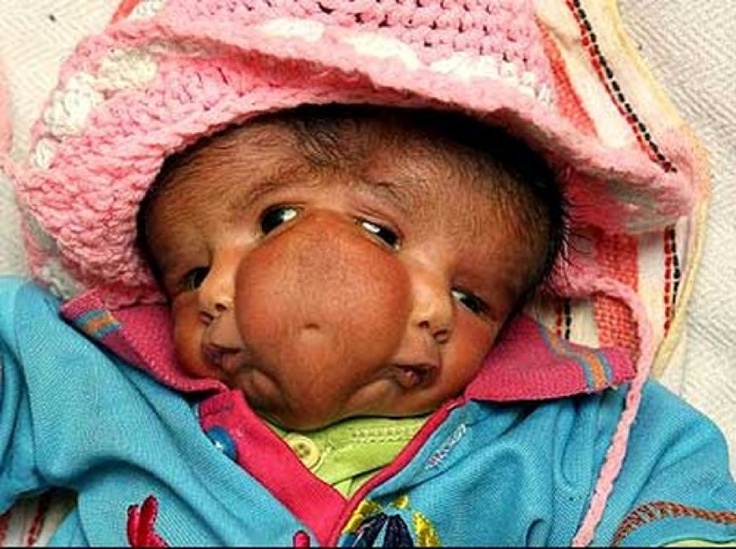
The marfanoid-progeroid-lipodystrophy syndrome MFLS is characterized by congenital lipodystrophy premature birth with an accelerated linear growth disproportionate to weight gain and progeroid appearance with distinct facial features including proptosis downslanting palpebral fissures and retrognathia. Jacquinet A Verloes A Callewaert B Coremans C Coucke P de Paepe A Kornak U Lebrun F Lombet J Pierard GE Robinson PN Symoens S Van Maldergem L Debray FG. They also typically have overly-flexible joints and scoliosis.
2016 by an unknown mechanism. The severity of the symptoms of MFS is variable. Marfanoidprogeroidlipodystrophy syndromeMPL also referred to as Marfan lipodystrophy syndrome MFLS is a variant of MFS in which Marfan symptoms are accompanied by features usually associated with neonatal progeroid syndrome also referred to as WiedemannRautenstrauch syndrome in which the levels of white adipose tissue are reduced.
Definition The marfanoid-progeroid-lipodystrophy syndrome MFLS is characterized by congenital lipodystrophy premature birth with an accelerated linear growth disproportionate to weight gain and progeroid appearance with distinct facial features including proptosis downslanting palpebral fissures and retrognathia. It also prevents her body from making enough asprosin. The medical condition is characterized by abnormal or degenerative conditions of the bodys adipose tissue.
A distinctive phenotype consisting of partial manifestations of Marfan syndrome a progeroid facial appearance and clinical features of lipodystrophy was present in all individuals. Also known as WiedemannRautenstrauch syndrome and severe partial lipodystrophy. Mutations in the fibrillin-1 gene lead to adipose tissue dysfunction and causes Marfan syndrome marfanoid progeroid lipodystrophy syndrome and neonatal progeroid syndrome.
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. A more specific term lipoatrophy is used when describing the loss of fat from one area. Jacquinet A Verloes A Callewaert B Coremans C Coucke P de Paepe A Kornak U Lebrun F Lombet J Pierard GE Robinson PN Symoens S Van Maldergem L Debray FG.
616914 - MARFANOID-PROGEROID-LIPODYSTROPHY SYNDROME. Lipodystrophy syndromes are a group of genetic or acquired disorders in which the body is unable to produce and maintain healthy fat tissue.
Lipodystrophy syndromes are a group of genetic or acquired disorders in which the body is unable to produce and maintain healthy fat tissue.
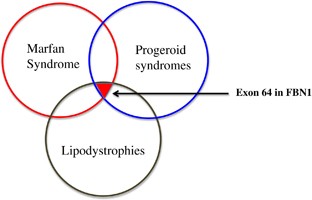
Also known as WiedemannRautenstrauch syndrome and severe partial lipodystrophy. Neonatal progeroid variant of Marfan syndrome with congenital lipodystrophy results from mutations at the 3 end of FBN1 gene. Also known as WiedemannRautenstrauch syndrome and severe partial lipodystrophy. The mutation mangles noses and makes Abby look prematurely old. MFLS To ensure long-term funding for the OMIM project we have diversified our revenue stream. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin with long arms legs fingers and toes. Although FBN1 knockout KO or dominant-negative mutant mice are widely used as an animal model for Marfan syndrome MFS these mice cannot recapitulate the genotypephenotype relationship of Marfanoid-progeroid-lipodystrophy MPL syndrome which is caused by a mutation in the C-terminus of fibrillin-1 the penultimate exon of the FBN1 gene. 2016 by an unknown mechanism. Lipodystrophy syndromes are a group of genetic or acquired disorders in which the body is unable to produce and maintain healthy fat tissue.
The medical condition is characterized by abnormal or degenerative conditions of the bodys adipose tissue. Neonatal progeroid variant of Marfan syndrome with congenital lipodystrophy results from mutations at the 3 end of FBN1 gene. The marfanoid-progeroid-lipodystrophy syndrome MFLS is characterized by congenital lipodystrophy premature birth with an accelerated linear growth disproportionate to weight gain and progeroid appearance with distinct facial features including proptosis downslanting palpebral fissures and retrognathia. It also prevents her body from making enough asprosin. A more specific term lipoatrophy is used when describing the loss of fat from one area. Marfanoidprogeroidlipodystrophy syndromeMPL also referred to as Marfan lipodystrophy syndrome MFLS is a variant of MFS in which Marfan symptoms are accompanied by features usually associated with neonatal progeroid syndrome also referred to as WiedemannRautenstrauch syndrome in which the levels of white adipose tissue are reduced. Mutations in the fibrillin-1 gene lead to adipose tissue dysfunction and causes Marfan syndrome marfanoid progeroid lipodystrophy syndrome and neonatal progeroid syndrome.





































Post a Comment for "Marfanoid–progeroid–lipodystrophy Syndrome"